Do you know what is Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM)
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 95 percent of all cases. Obesity is the primary cause for Type II diabetes mellitus and the alarming rise in diabetes prevalence throughout the world has been in direct association increase rates of obesity worldwide. Type II diabetes mellitus leads to many health problems including cardiovascular disease, stroke, blindness, kidney failure, neuropathy, amputations, impotency, depression, cognitive decline and mortality risk from certain forms of cancer.
 Current therapy for type 2 diabetes includes lifestyle intervention (weight-loss, appropriate diet, exercise) and anti-diabetes medications. Medical supervision and strict adherence to the prescribed diabetes treatment regimen may help to keep blood sugar levels from being excessively high although medications and lifestyle changes cause remission of the disease.
Current therapy for type 2 diabetes includes lifestyle intervention (weight-loss, appropriate diet, exercise) and anti-diabetes medications. Medical supervision and strict adherence to the prescribed diabetes treatment regimen may help to keep blood sugar levels from being excessively high although medications and lifestyle changes cause remission of the disease.
In fact, Type II diabetes mellitus often worsens with time, requiring even greater numbers of medication or a higher dosage to keep blood sugar under control. For this reason, Type II diabetes mellitus has been considered a chronic and progressive disease.
Did you know?
- Someone in the world dies from complications associated with diabetes every 10 seconds. Diabetes is one of the top ten leading causes of deaths.
- Diabetics have health expenditures that are 2.3 times higher than non-diabetics.
- Approximately 90 percent of type 2 diabetes mellitus (the most common form of diabetes) is attributable to excessive body fat.
- If current trends continue, Type II diabetes mellitus or pre diabetic conditions will strike as many as half of adult people by the end of the decade.
- The prevalence of diabetes is 8.9 percent for the population but more than 25 percent among individuals with severe obesity.
- Metabolic and bariatric surgery is the most effective treatment for Type II diabetes mellitus among individuals who are affected by obesity and may result in remission or improvement in nearly all cases.
What is Transit Bipartition surgery?
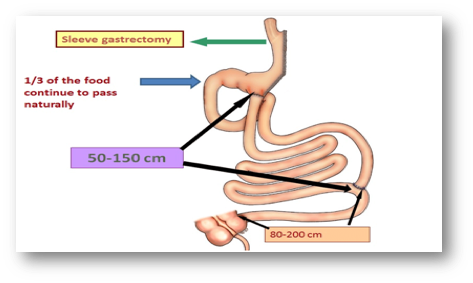
Transit bipartition is a metabolic surgical method developed for the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. It was developed 10 years ago by Santoro in Brazil and has been widely accepted. In this surgery the entire distal part of small bowel is brought to the lower stomach and a second exit is provided, therefore all the food can pass through the entire small bowel segments.
Which type of diabetics undertake Transit Bipartition surgery?
The first requirement is that the patient has type 2 diabetes. Then it is looked at whether the insulin reserve is enough. If the patient also meets this condition, then the patient is fully matched by looking for more specific conditions. In type 1 diabetes patients, neither metabolic surgery nor bariatric surgery can be performed.
How long will the surgery last?
The duration of the operation may be extended but it usually ends in a period of 4 to 6 hours. Although it may seem like a difficult operation the number of surgeons successfully perform the surgery in a high level and adequate hospitals.
How is it performed?
Like all obesity and metabolic surgical procedures performed today, this operation is performed by laparoscopic method. Transit bipartition surgery requires more laparoscopic surgery experience, skills and experience compared to sleeve gastrectomy.
Recovery after surgery
You will need to follow the diet after surgery. Dietician will explain what you can eat during the first few months after surgery. In 3-5 weeks you will be able to start working and all other activities you used to do during normal daily life. The weight loss will be finished approximately in one or one and half years. You will need to check your blood level and eat good healthy food.

